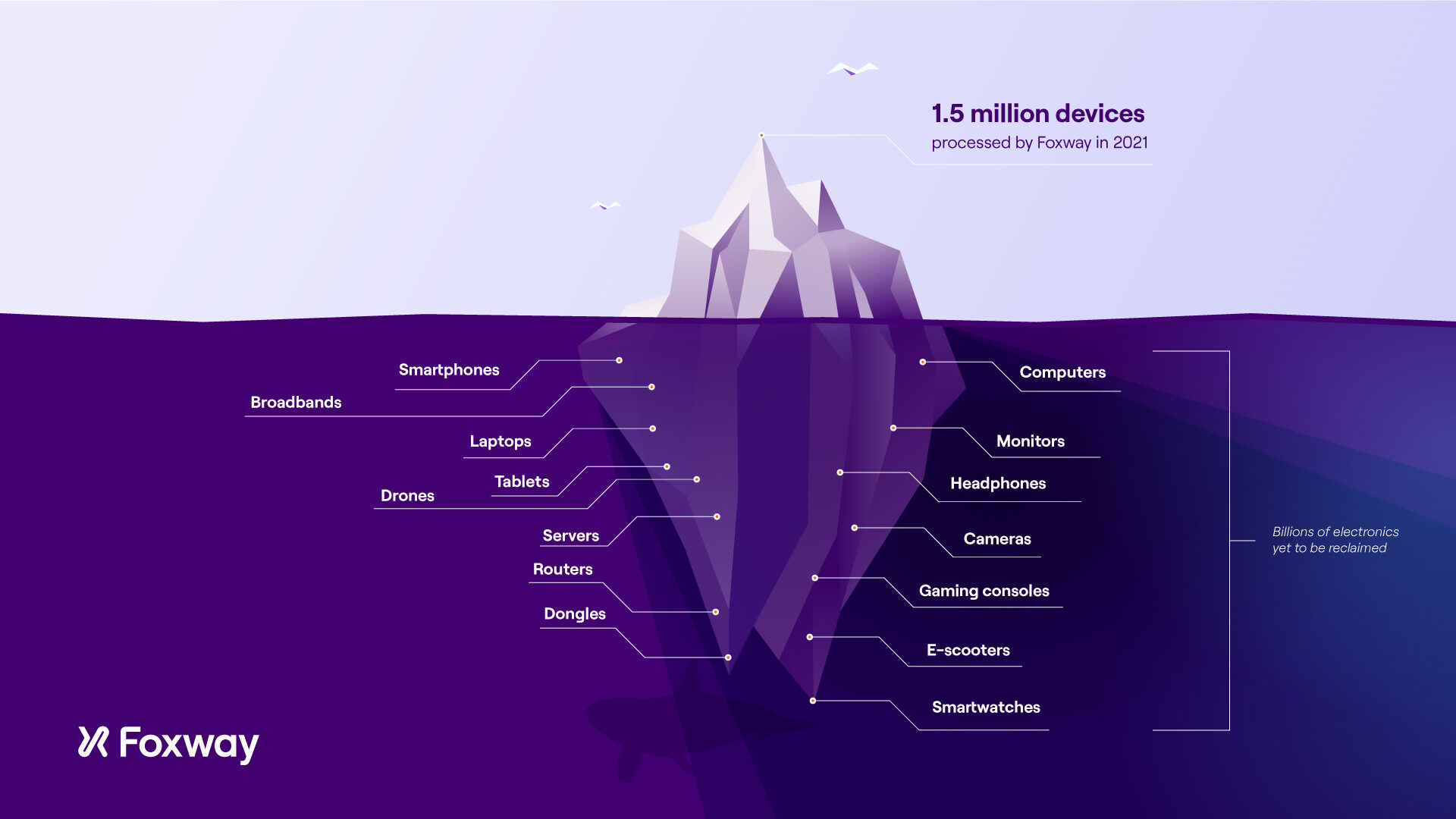
The quantities of ICT hardware continue to grow worldwide. In 2021, the number of mobile devices operating worldwide stood at almost 15 billion. In comparison, the world’s population is around 8 billion.
So, where are these electronics? End-users hold 2-3 devices per capita, while organizations shelve electronics in bulk. On average, these products are in use only for a few years. When electronics reach their End-of-Life (EOL), that doesn’t mean they’re useless. On the contrary, there is a solution for sustainable end-of-life management.
Recycling is a sustainable alternative to disposal
Resource extraction and CO2 emissions occur at every stage of the ICT device lifecycle. Each stage produces residues, and the negative environmental impact is heaviest at the initial production. Therefore, we can ease the environmental burden by extending device lifetime and prolonging the demand for brand new production.
Used electronics house multiple components and valuable raw materials suitable for recycling. Components can be used as spare parts and materials end up in the makeup of new devices. Our teams continually improve processes ensuring that all equipment lasts longer and that resources don’t go to waste.
“We’re managing retired IT assets in a greener way and returning hardware to the circular economy. This is a standard practice in modern organizations. At the same time, many companies have yet to get started.“
Mikkel Frid, Sourcing Director
Smart asset management is a way to implement corporate responsibility. Organizations can enable sustainability through reverse logistics and get value back at the end of device lifecycle. Detailed reporting, in return, helps you be environmentally accountable.
How to streamline your electronics reuse?
Effective EOL asset management is a combination of identification and quality processes. Typically, organizations sell their EOL inventory to a refurbishment or recycling partner. The following steps will help you find a suitable partner.
STEP #1: Inventory of your IT assets
The first step of successful EOL management is the inventory of retired assets. Begin by identifying all the excess IT devices generated within your organization. An accurate IT asset inventory leads to a better recovery of the devices. Sometimes the devices that seem only suitable for disposal can be recycled. For example, most of the used devices sold to Foxway live a second life through our remarketing network.
Choose a partner who can both extend device lifetime and do proper disposal. This will increase your revenue and support the profitable circular economy.
STEP #2: Positive environmental impact in writing
Successful EOL management has a positive environmental impact. The environmental benefits come from reuse, and recycling, and the proper disposal of ICT equipment. Each service brings us closer to a more sustainable world.
If you care about your company’s impact in writing, Foxway provides a report on recycling and reuse. The documentation will display the allocation of your EOL electronics, alongside your company’s positive environmental impact.
STEP #3: Regulatory compliance is your peace of mind
Electronic devices containing potentially harmful materials are considered hazardous waste and should be recycled. Within the European Union, device recycling should comply with the Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive. The framework regulates collection and recycling of electrical goods with a particular emphasis on reuse and material recovery.
Used electronics destined for refurbishment and reuse are also considered e-waste. However, instead of landfills, these electronics can enter the circular economy. While each country can implement their own regulations, consider referencing the WEEE Directive when looking for a partner within Europe.
The leading circular economy enabler
Foxway advocates for giving devices a second life. We aspire to help our customers get closer to the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. To achieve this, we reclaim value from your electronic assets throughout the device lifecycle. Device recycling entails:
- Logistics and warehousing
- Assessing residual value
- Certified data wipe
- Testing, refurbishing and grading the devices for resale
- Sending recyclable components and raw materials to collection partners
- Device allocation and sustainability reporting
Reuse can be transparent and streamlined. When devices live longer, more people can benefit from access to technology.
ICT-devices Buyback Sustainability Electronic Waste Reuse



